How is A.I. Changing the Arts
Humanity has long used technology to enhance and augment the creation of art. Each new invention has shifted how we experience and interpret artistic expression from the paintbrush to the camera. And now, with the rise of artificial intelligence, we are seeing yet another revolution in the world of the arts.
A.I. is disrupting various industries and sectors, and the arts are no exception. From the visual arts to music composition, A.I. is used in many ways. We’re even seeing it used in more technical areas, such as film editing and writing.
In this blog post, we’ll explore a few ways A.I. is impacting the arts and its implications for creators and consumers alike.
Table of contents
One way A.I. is making its mark on the visual arts is through the creation of so-called “A.I. art generators.” These computer programs use algorithms to generate unique and often visually stunning art pieces. Originally developed for commercial purposes, such as creating graphics for advertisements, the fine art world is now embracing these A.I. art generators.
But how do they work? In essence, these programs start with a database of images and use machine learning to manipulate and combine them into new compositions. They can also take inspiration from famous artists or works of art or even generate original pieces based on mathematical equations.
The entire process rests heavily on the initial training of the A.I., as well as human input in terms of choosing which images or inspirations to use. For example, an A.I. art generator trained in the works of Monet may produce very different results than one trained in contemporary street art.
Pixel by pixel, A.I. art generators can create intriguing and visually striking works of art. It raises the question: can a machine truly create art, or is it merely mimicking human creativity? After all, even human artists draw inspiration from those who have come before them and use various techniques and tools to create their work.
To answer the question of whether A.I.-generated art can be considered “real” art, let’s first define art. At the end of the day, art is about personal interpretation and individual taste. A piece that can move and inspire one person may leave another feeling apathetic. However, when something creates strong reactions and discourse, it’s hard to argue that it isn’t art.
In recent years, A.I.-generated pieces have sparked controversy and drawn attention at art shows and exhibitions worldwide. One such piece is “The Next Rembrandt,” a 3D-printed painting created by Microsoft in partnership with the Rembrandt House Museum in Amsterdam. The A.I. analyzed hundreds of Rembrandt’s works to create a unique composition, down to the brushstrokes and texture.
Another standout example is “Théâtre D’opéra Spatial,” by A.I. artist Jason Allen. Using the Mid-journey neural network, Allen created a stunning mix of classical and futuristic aesthetics. The reason it went viral was that it actually won the Colorado State Fair art competition, beating out traditional human artists.
These examples show that A.I.-generated artwork can stir up debate and elicit strong reactions, making it no different from any other piece of art. And with the technology improving every day, we’ll likely see more and more A.I.-generated works making their mark on the art world.
Most Expensive Pieces Of AI ART
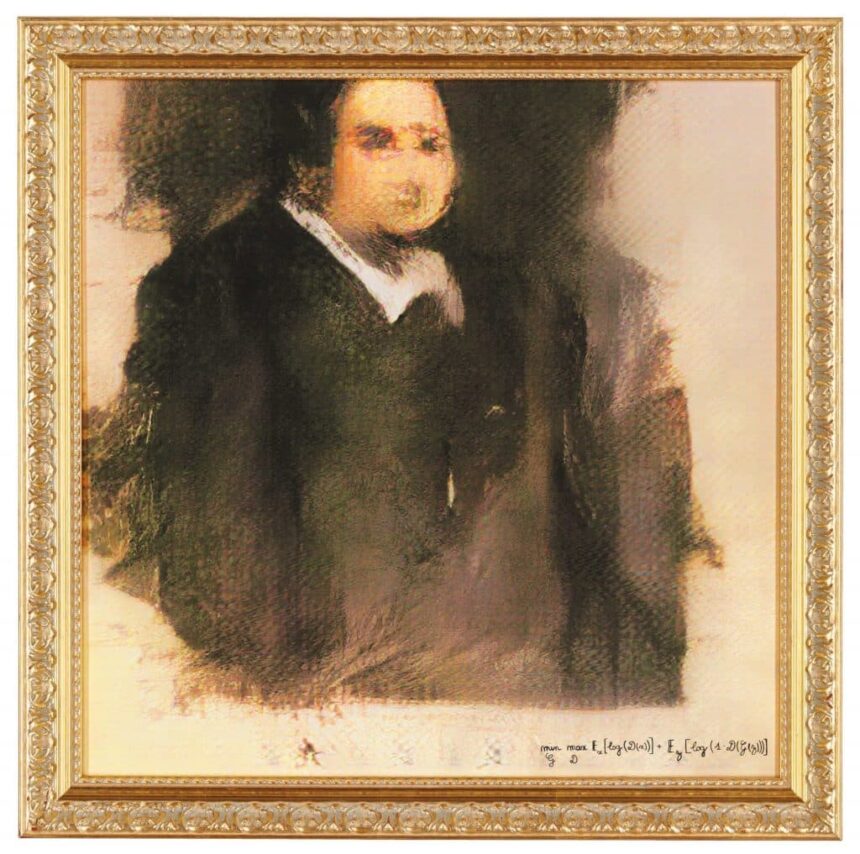
The most expensive piece of AI art is the portrait called “Edmond de Belamy” sold for staggering USD 432,000 at Christie’s auction house in New York City.
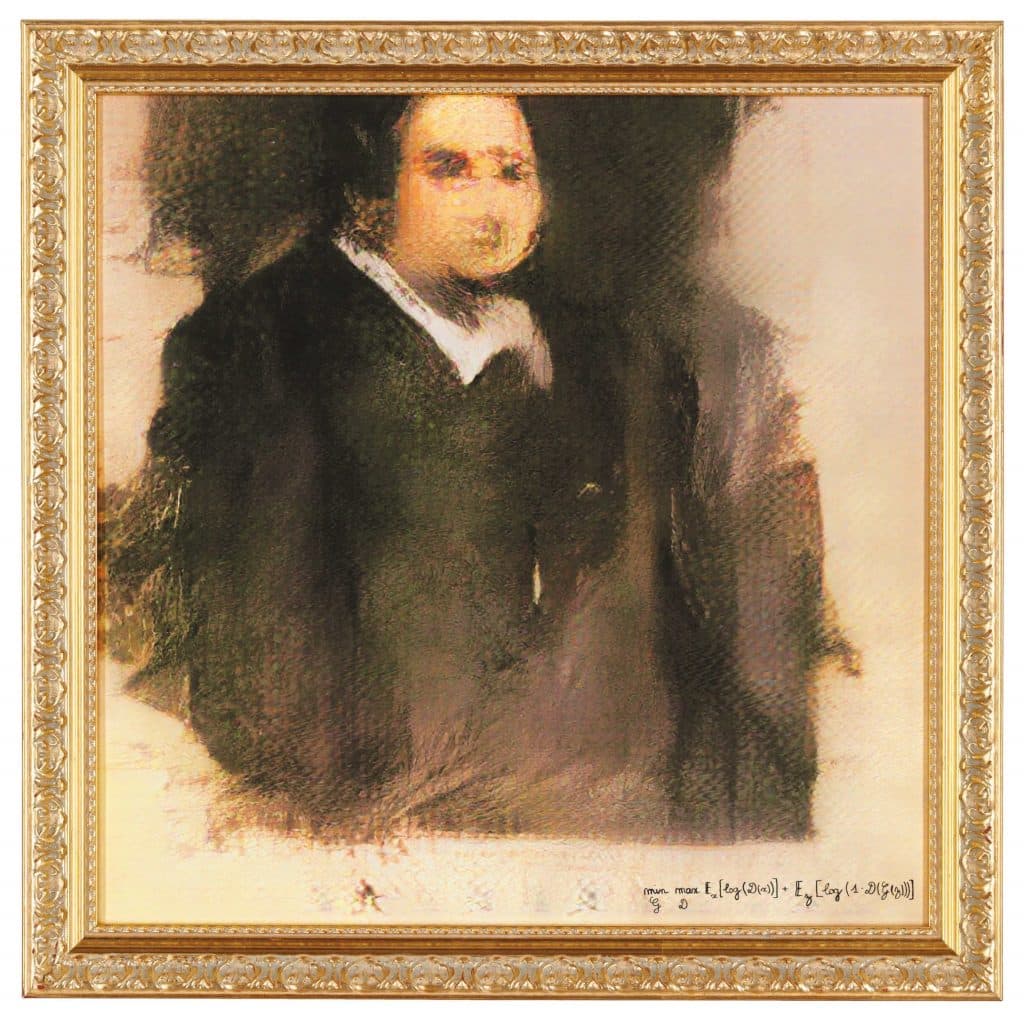

Last fall, an AI-generated portrait rocked the art world selling for a staggering US$432,500 at Christie’s auction house in New York. The portrait called “Edmond de Belamy” features a slightly out-of-focus man with no nose and a blob for a mouth, dressed in what seems to be a dark frock-coat over a white-collared shirt.
From a distance, the 70 cm by 70 cm portrait printed on canvas and hung in a gilded wood frame, looks like it belongs in a museum of classical art. But upon closer inspection, the artist’s signature — the mathematical formula that created it (min G max D x [log (D(x))] + z [log (1 – D (G(z)))]) — reveals that the artist was not human.
How Do AI Art Generators Work?
AI generated art is a relatively new field of art that is currently stretching the boundaries of creativity and is disrupting how art is actually made. Artists can now use an advanced machine learning model to generate new visual works. The images created by this these are called AI-generated images. This process is able to generate unique artwork the likes of which the world has never seen! We are already seeing computer generated art in art galleries and even on music album covers.
Can I Build My Own AI Art Generator?
Since A.I. art generators rely heavily on machine learning and algorithms, they can be difficult to create without a background in computer programming. However, there are some resources available for those interested in experimenting with A.I. generated art. Here are a few terms and tools to start with:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These are algorithms used in machine learning that pit two neural networks against each other, one generating samples and the other trying to distinguish between real and A.I. generated data. GANs have been used in everything from image generation to voice creation.
- Contrastive Image Language Pretraining (CLIP): A recent breakthrough in A.I. image generation, CLIP combines language and visual representation to generate unique images based on text input.
- Vector Quantized GAN (VQGAN) and StyleGAN: Two popular GAN models used for generating high-resolution images.
- GPT-3: An advanced language processing A.I. developed by OpenAI, GPT-3 can generate text in a variety of styles and formats, including poetry and music lyrics. GPT-3 is the most advanced language A.I., allowing your bot to truly understand you.
Mixing and experimenting with these tools allows you to create your own A.I.-generated artwork. You’ll need to brush up on your coding skills and have a strong understanding of machine learning, but the potential for unique and thought-provoking artwork is certainly there. Essentially, the steps to creating your own A.I. art generator would be as follows:
- Familiarize yourself with the tools and resources mentioned above
- Gather a dataset to train your A.I. on, such as images or text
- Use a GAN model to generate unique images or text based on the training data
- Experiment and fine-tune your results until you have something you’re happy with
If building your own A.I. art generator from scratch sounds like too much work, there are plenty of online tools to explore and play with. Here are some of the best:
1. Deep Dream Generator:
This website allows you to upload your own image and transform it into a dreamlike, psychedelic piece using A.I. algorithms. Google’s Deep Dream algorithm enhances patterns and colors in the image, creating a trippy and unique result.
2. DALL-E:
Another tool by OpenAI, DALL-E 2, can generate images based on text input. Simply type in a description or concept, and the A.I. will create a picture to match. For example, typing in “a cat sitting on top of a pizza” results in exactly that—a cat lounging atop a slice of pepperoni pizza. DALL-E is recognized for its frighteningly realistic images and attention to detail.
3. RunwayML:
Similar to DALL-E, RunwayML allows you to generate images based on a text input or create various visual effects using A.I. algorithms. However, it takes things one step further by allowing users to create animations and 3d models using A.I. With a robust video editor and various filters and effects, RunwayML offers endless potential for A.I. generated art.
4. WOMBO Dream:
When the NFT craze hit, WOMBO wanted in on the action. This Canadian website allows users to generate an NFT using A.I.-generated artwork, complete with a unique title and description. The resulting artworks are bizarre and often surreal, making them highly sought after by collectors.
Another area where A.I. is making an impact is in the music industry. Like with visual art, A.I. can generate unique music or even create entire albums. Once again, machine learning algorithms are used to analyze and develop new melodies, harmonies, and lyrics. Everything is based on training data, such as existing music from a specific genre or even a composer’s previous work.
However, music isn’t all about melodies and instruments—there’s also the performance element. A.I. is also making its mark here with technologies such as voice synthesis and virtual singers. It can match the tone and inflection of a natural human voice, allowing A.I.-generated music to sound even more realistic.
Finally, we go back to the natural language processing we mentioned earlier. A.I. is not just capable of creating text but also generating music lyrics. GPT-3 can understand rhyme scheme, meter, and other stylistic elements that make a song sound cohesive and polished.
As of now, AI-generated music hasn’t garnered the same level of attention and recognition as A.I. generated visual art. It has mainly been limited to repetitive pop songs or experimental albums. But with advancements in technology, it’s only a matter of time before we turn on the radio to hear a catchy tune composed entirely by A.I.
So, where can you start creating A.I. music? Here are a few tools and resources to explore:
1. Jukebox
As you might have guessed by now, OpenAI is pretty much the industry leader in all things AI. Their tool, Jukebox, allows users to generate music in various genres, from pop to jazz to rock. The A.I. is trained in the musical styles of famous artists, allowing for some awe-inspiring results.
2. Amper Music
Amper is a cloud-based platform that allows users to create custom music using A.I. Users can select specific instruments, moods, and genres to generate unique tracks for their projects. Mostly aimed at video game and movie soundtrack creators, Amper is simplifying the music composition process.
3. Solaris Virtual Vocalist
Powered by Synthesizer V, Solaris offers virtual singers that can perform vocals in native English and various other languages. Users can input lyrics, and the virtual vocalist will perform them, adding emotion and personality to A.I.-generated music. A real singer can then use Solaris as a guide for their own vocal performance, or the virtual vocalist can be used as is.
4. A.I. Duet
Finally, Google joins the party with its A.I. Duet tool. It may not be as advanced as other tools, but it’s a fun and easy way to explore A.I.-generated music. It’s a simple concept—the user plays a melody on the piano, and the A.I. responds with its own harmonic improvisation.
Advanced Content on Artificial Intelligence and The Arts:
Conclusion
As A.I. continues to advance, we see its impact in industries such as the arts. It’s creating unique visual works and compositions, challenging the notion of what it means to be an “artist.” And while there may be some concern about A.I. taking over human creativity, for now, it is simply offering another tool for artists to explore and push the boundaries of their craft.
So, what do you think? Would you be interested in trying out A.I.-generated music or visual art?
References
Hageback, Niklas, and Daniel Hedblom. AI for Arts. CRC Press, 2021.
Hirsch, Andreas J., et al. The Practice of Art and AI: European ARTificial Intelligence Lab. Hatje Cantz, 2022.
Miller, Arthur I. The Artist in the Machine: The World of AI-Powered Creativity. MIT Press, 2020.
Zylinska, Joanna. AI Art: Machine Visions and Warped Dreams. 2020.