Introduction
If you have ever worked on an electric motor, there is a pretty high chance you have come across Fleming’s Left Hand Rule. This rule is named after an electrical engineer and physicist named Sir John Ambrose Fleming.
He was known as the inventor of the vacuum tube and the one who established something called the right hand rule in physics during the 19th century. So now that we know a little about Fleming, what exactly is Fleming’s Left Hand Rule?
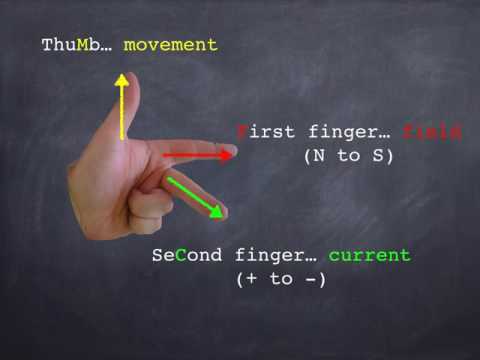
Fleming’s left-hand rule is a simple mnemonic that is used to determine the direction of the induced current in an electric motor. The rule states that if you extend the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of your left hand so that they are mutually at right angles, then the direction in which the thumb points is the direction of the current that is induced in the motor. The forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field, and the middle finger indicates the direction of motion.
In more detail, when a conductor is placed in a magnetic field, an electromotive force (EMF) is induced in the conductor that is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the conductor. This induced EMF results in an induced current flowing in the conductor. The direction of the induced current is determined by the direction of the EMF, which is given by Lenz’s Law. Lenz’s Law states that the induced current will be in such a direction that the magnetic field it creates will oppose the change in the magnetic field that produced it.
In summary, Fleming’s left-hand rule helps to determine the direction of the induced current in a motor, by showing the direction of thumb, forefinger and middle finger as the direction of current, magnetic field and motion respectively.
Well it is used to accurately find the direction of force or motion of a conductor within an electric motor in a simple way. This rule can only be applied though when the magnetic field direction and the current direction are already known, so it can’t be used for stepper motors, brushless DC motors, servo motors, or brushless motors. To get more background information we will first start with what a motor is.