Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the intelligence process of creating unique systems using algorithms and software that can complete tasks without the need for human interaction and instructions. Artificial intelligence includes machine learning, natural language processing, reasoning, and perception. AI in diagnostic helps replicate human cognition and assess complex medical and diagnostic data represented in graphs and images. The technology is majorly used to study the association between treatment procedures and patient results.
Table of contents
Enhancing Image Analysis: AI in Radiology and Pathology Diagnostics
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds a transformative potential in the field of radiology and pathology, where it is revolutionizing the way we analyze medical images. Through machine learning algorithms and deep learning networks, AI can assist in interpreting a broad spectrum of diagnostic imaging – including X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and pathology slides. These technologies go beyond human capabilities, analyzing images in minute detail, detecting abnormalities or patterns that can be easily overlooked by human eyes, and aiding in early detection and diagnosis of various conditions such as cancer, fractures, and neurological disorders.
In pathology, AI holds the promise to transform traditional microscopy. By digitizing slides and using AI algorithms to analyze them, we can streamline the diagnostic process and improve its accuracy. For instance, AI can be used to differentiate between various cell types, identify abnormal cell structures, and quantify biomarkers, helping pathologists make more informed decisions. This level of automation not only saves time and resources but also reduces the chances of human error. This AI-enhanced approach has already shown impressive results in diagnosing conditions such as breast cancer, skin cancer, and various hematological diseases.
Predictive Analysis: AI’s Role in Forecasting Disease Progression
Predictive analysis using artificial intelligence is an emerging field with significant potential to transform healthcare. AI algorithms, particularly those using machine learning, are capable of handling vast amounts of data and identifying patterns that may not be visible to the human eye. This capability is particularly relevant when it comes to predicting the progression of diseases. By analyzing patient data, clinical histories, genetic information, and even data on lifestyle factors, AI can provide predictions about how a disease may progress in a specific patient, enabling personalized treatment plans and potentially improving outcomes.
AI’s role in predicting disease progression is particularly valuable in chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, or cancer, where early intervention can significantly impact the patient’s prognosis. Machine learning models can integrate diverse data sources to predict risks, suggesting when medical intervention might be necessary. For instance, AI models are being developed to predict the progression of Alzheimer’s disease by analyzing neuroimaging data and cognitive test scores. Similarly, in oncology, predictive models are being used to forecast tumor growth and response to treatment. These predictive capabilities of AI not only hold the promise of improved patient care but also offer potential cost savings by optimizing treatment strategies and minimizing unnecessary interventions.
Precision Medicine: Tailored Treatments through AI Diagnostics
Precision medicine is a medical approach that takes into account individual variability in genes, environment, and lifestyle when designing therapeutic interventions. In this context, artificial intelligence has emerged as a crucial enabler, allowing for a level of data analysis and interpretation that is far beyond human capabilities. AI can process and interpret vast amounts of patient data – from genetic sequences to electronic health records – enabling healthcare professionals to make more precise diagnoses and treatment decisions. This tailored approach helps to maximize effectiveness and minimize potential side effects, leading to improved patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare systems.
The application of AI in precision medicine extends to various fields such as oncology, cardiology, neurology, and more. In cancer treatment, for example, AI can help identify genetic mutations and patterns that may suggest a person’s likelihood to respond to specific therapies. AI can aid in the analysis of medical images to detect early signs of diseases like cancer or heart disease, enabling intervention at a stage where treatment can be most effective. In these ways, AI is playing a transformative role in realizing the full potential of precision medicine, leading to treatments that are tailored to the individual and significantly improving the quality of care.
AI in Genetic Diagnostics: Unlocking the Potential of Genomic Data
Genetic diagnostics involves the analysis of genetic data to detect anomalies linked to diseases, and this field has been transformed by the advent of artificial intelligence. The human genome is composed of over 3 billion base pairs, and sifting through this immense dataset for clinically significant mutations is a task well suited to AI. Machine learning algorithms can analyze this vast quantity of genomic data and detect patterns or anomalies that could signify genetic diseases or predispositions. This can enable the early diagnosis of conditions such as cancer, heart disease, or rare genetic disorders, leading to timely and targeted treatments.
AI also plays a significant role in understanding how different genes interact with each other and with environmental factors to cause disease. By applying AI algorithms to large genomic datasets, researchers can identify complex genetic interactions that may underlie multifactorial diseases. This can lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies, such as gene therapies that target specific genetic alterations. In summary, AI’s ability to process and interpret vast amounts of genomic data is unlocking new possibilities in genetic diagnostics and personalized medicine.
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy: The Role of Machine Learning
The accuracy of diagnostic processes is fundamental to effective healthcare. Machine learning, a subset of AI, is playing a pivotal role in enhancing diagnostic accuracy across a wide spectrum of medical specialties. Machine learning algorithms, trained on vast datasets, can recognize patterns and anomalies within complex data that may be imperceptible to the human eye. These algorithms can aid in detecting conditions ranging from skin cancer to pneumonia in chest X-rays with impressive accuracy, often on par with or exceeding that of human clinicians. By integrating machine learning into diagnostic workflows, clinicians can make more informed decisions, reduce the likelihood of false negatives and positives, and ultimately deliver more precise and personalized care.
Machine learning can contribute to the reduction of diagnostic errors, which are a significant concern in healthcare. It can achieve this by serving as a second opinion or decision support tool for healthcare professionals, who may sometimes make mistakes due to fatigue, cognitive biases, or the inherent complexity of certain cases. Machine learning algorithms, which remain unaffected by such human limitations, can provide objective assessments, helping to validate or challenge human-made diagnoses. In essence, machine learning promises to be a powerful tool in enhancing diagnostic accuracy, with the potential to improve patient outcomes significantly.
Speeding Up Diagnosis: AI’s Impact on Time-Sensitive Conditions
The rapid evolution of AI-based technologies has had a remarkable impact on speeding up diagnoses of time-sensitive conditions, leading to improved health outcomes. For instance, the use of AI in medical imaging has proven to be an indispensable tool for detecting anomalies swiftly and accurately, enabling timely intervention. The unprecedented market growth of the software segment is a testament to the increasing reliance on these innovative technologies within healthcare. AI-based technologies not only enhance efficiency but also lead to more accurate diagnoses, which is particularly crucial in time-sensitive conditions.
Government initiatives supporting the adoption of advanced technologies in healthcare have significantly contributed to the largest market share held by AI in diagnostics. Traditional machine learning, a critical component of AI-based diagnostics, has been refined and optimized to analyze vast amounts of data swiftly and provide crucial insights, thereby reducing diagnosis times dramatically. As these initiatives continue to encourage the use of AI-based technologies, we can expect even faster and more accurate diagnoses, fundamentally transforming the approach to managing time-sensitive conditions.
Also Read: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Business Process Improvement
AI in Mental Health: Predicting and Diagnosing Mental Disorders
The application of AI in the realm of mental health is an emerging field that has the potential to drastically alter how mental disorders are predicted and diagnosed. Traditionally, mental health diagnoses have relied heavily on subjective assessments such as patient interviews and self-reported symptoms. However, AI’s data-driven approach allows for the analysis of a more comprehensive range of factors, including genetic data, brain imaging, and behavioral patterns, to generate more precise diagnoses. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to identify subtle patterns or symptom correlations that may be difficult for clinicians to detect, enabling earlier detection and intervention of mental disorders.
In addition to diagnosis, AI holds significant promise in the realm of predicting mental health disorders. Predictive models built on large datasets can help identify individuals at risk of developing mental health issues even before symptoms manifest. This aspect of AI can be particularly useful in conditions such as depression and anxiety, where early intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes. Through the use of AI, we can move towards more proactive mental healthcare, where the focus shifts from response to prediction and prevention.
AI in Telemedicine: Remote Diagnostics and Monitoring
AI’s role in telemedicine has emerged as a crucial component of remote diagnostics and monitoring, especially in light of the recent global pandemic, which underscored the importance of healthcare accessibility irrespective of geographical location. With AI-powered tools, doctors can monitor patients’ health status remotely, analyze health data in real-time, and provide accurate diagnoses without the need for physical presence. For instance, AI can analyze data from wearable devices to monitor vital signs, detect abnormalities, and alert healthcare providers of potential health concerns. These capabilities can be particularly advantageous in managing chronic conditions, where consistent monitoring is essential.
In addition to remote monitoring, AI also enables enhanced remote diagnostics, which can dramatically improve healthcare delivery in remote and underserved areas. AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays or CT scans, to detect diseases ranging from pneumonia to cancer, even when specialized doctors are not available. These systems can be trained to match, or even surpass, the diagnostic accuracy of human experts, thereby ensuring that quality care is not confined to areas with a high concentration of specialists. AI in telemedicine is not just about bringing healthcare to more people; it’s about ensuring the delivery of high-quality, personalized care, irrespective of location.
Early Disease Detection: AI’s Preventive Role in Healthcare
The ability to detect diseases at an early stage is a game-changer in healthcare, and AI is playing an increasingly significant role in this area. By analyzing a wide array of data from electronic health records, genetic tests, and wearable devices, AI algorithms can identify subtle patterns that might be indicative of the early stages of diseases. These patterns could be overlooked by human practitioners, especially when they are not apparent in the context of conventional diagnostic tests. This capacity of AI for early disease detection can be crucial in cases like cancer, heart diseases, or neurological disorders, where early intervention can dramatically improve patient outcomes and potentially save lives.
AI’s preventive role in healthcare extends beyond early disease detection, too. Predictive analytics algorithms can be used to assess patient risk for various conditions based on their medical history, lifestyle factors, and even genomic information. With this information, healthcare providers can work with patients to devise personalized preventive care plans. This could include lifestyle modifications, routine screenings, or preventive medication, tailored to each individual’s specific risk factors. By taking a proactive approach to health management, AI is helping to shift the healthcare paradigm from a largely reactive system to one focused on prevention and early intervention.
Also Read: How Can 3D Imaging Improve Medical Imaging and Diagnoses
Overcoming Diagnostic Challenges: AI in Rare Disease Identification
The diagnosis of rare diseases often presents a daunting challenge in medical practice, owing to the scarcity of cases, lack of awareness, and complex symptomatology. AI-based solutions are stepping up to address these obstacles, streamlining the process of identifying rare diseases. Leveraging deep learning technology, AI systems can analyze comprehensive datasets from patient records, including imaging scans, genetic data, and clinical notes. Through pattern recognition and predictive modeling, these systems can then pinpoint the subtle indicators of rare neurological diseases and other conditions. This not only enhances accurate diagnosis, but it also facilitates the crafting of individual patient treatment plans, significantly impacting clinical outcomes.
AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data at high speeds plays a pivotal role in the drug development process, particularly in the realm of rare diseases. By analyzing patient records and the latest research, AI can expedite the drug discovery process and contribute to the development of effective treatments that might otherwise take years to emerge. This integration of AI into clinical practice is expected to drive the fastest growth rate in healthcare, reducing healthcare costs, and improving the quality of care. Key factors behind this growth include the efficiency gains in clinical processes, the improvement in clinical documentation, and the potential of AI to offer medical practitioners unprecedented insights into their patients’ conditions.
Conclusion
The healthcare sector is widely adopting artificial intelligence (AI)-powered solutions to obtain higher operational & functional results. This factor is supporting the growth of Artificial intelligence (AI) in the diagnostics market. Growing demand for advanced imaging methodologies for patient diagnostics is further driving market growth. Also, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases globally is fueling the demand for automated, innovative processes, which is boosting market expansion.
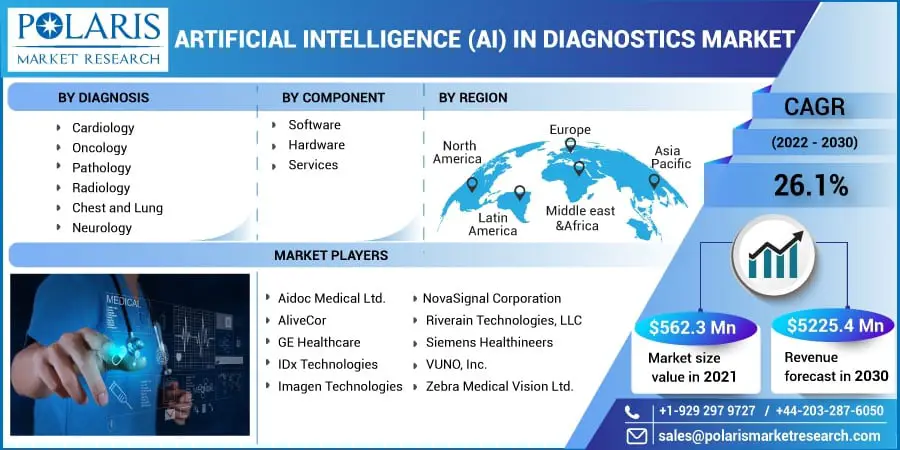
According to a research report published by Polaris Market Research, the global Artificial Intelligence (AI) in diagnostics market was valued at USD 562.3 million in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 5,225.4 Million By 2030, growing at a CAGR of 26.1% during the forecast period.
The government globally continuously offers favorable government initiatives to encourage healthcare providers and other healthcare firms to embrace AI-based diagnostic technologies. This factor is propelling the growth of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostics market. Growing spending by nonprofit companies and private organizations in order to obtain higher functional results and cost reductions are the key factors further expected to accelerate market growth over the forecast period.
Moreover, the rising application of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare devices due to the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease is then fueling the growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in diagnostics market. In addition, the increasing demand for improving patient care and reducing machine downtime is another crucial factor propelling the market growth.
Based on components, the market is segmented into hardware, software, and services. The software segment witnessed the largest market share in the global artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostics market in 2021 and is anticipated to continue its dominance over the projected period. The growing demand for AI-enabled solutions to deliver accurate diagnosis is one of the major factors boosting the segment’s growth. Also, the rapid adoption of AI technology to diagnose a wide array of acute and chronic diseases is further expected to fuel the demand for advanced AI-enabled solutions.
Based on the diagnosis, the market is categorized into Radiology, Oncology, Neurology, Cardiology, Chest & Lungs, Pathology, and Others. The neurology segment is anticipated to account for the highest market share in the artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostics market over the foreseen period due to the rising adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) based devices in neuro-degeneration of various neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). AI-based diagnostic solutions in neurology practice provide improved precision & accuracy, which is expected to have a huge demand in the healthcare industry.
Based on geography, North America is expected to witness the largest share in the global market owing to the increased focus on technological advancements. Various players, healthcare providers, and life sciences companies in the region are employing different types of AI, thereby accelerating the growth of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostics market. Also, other factors such as growing digital literacy, the emergence of startups, favorable government initiatives, and increasing funding are expected to augment market growth.
On the other hand, the Asia Pacific region is projected to generate the fastest growth during the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to the growing elderly population coupled with the rising prevalence of diseases such as cancer and stroke. Moreover, growing initiatives by public and private firms for encouraging the adoption of AI-based diagnostic solutions are expected to fuel the expansion of the global artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostics market.